declare @CurrentRow int
declare @TotalRows int
declare @FirstName nvarchar(255)
select @CurrentRow = 1
declare @TableVariable table
(
UniqueRowID int IDENTITY (1, 1) Primary key NOT NULL ,
FirstName nvarchar(255)
)
insert into @TableVariable (FirstName) values ('Adam')
insert into @TableVariable (FirstName) values ('Bill')
insert into @TableVariable (FirstName) values ('Charlie')
insert into @TableVariable (FirstName) values ('Dennis')
select @TotalRows=count(*) from @TableVariable
while @CurrentRow <= @TotalRows
begin
select @FirstName = FirstName
from @TableVariable
where UniqueRowID = @CurrentRow
print @FirstName
select @CurrentRow = @CurrentRow + 1
end
Tuesday, 19 December 2006
Cursor functionality via table variable and loop
Friday, 15 December 2006
Indexes : Included Columns
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX IndexName ON Schema.TableName (ID ,int1 ,int2 ,text1 ,text2 ,text3 ,text4 ,text5)
Warning! The maximum key length is 900 bytes. The index 'IndexName' has maximum length of 938 bytes. For some combination of large values, the insert/update operation will fail.
The way round this in sql 2005+ - INCLUDED COLUMNS
Add the column as an included column >
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX IndexName ON Schema.TableName (ID) INCLUDE (int1 ,int2 ,text1 ,text2 ,text3 ,text4 ,text5)
Thursday, 14 December 2006
Counts of database objects
-- sql 2005 - database object counts
if object_id('tempdb..#objecttypes') is not null
begin
drop table #objecttypes
end
create table #objecttypes (otype char(5)collate Latin1_General_CI_AS ,typedesc varchar(50),primary key clustered(otype))
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('AF','Aggregate function (CLR)')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('C','Check constraint')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('D','Default (constraint or stand-alone)')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('F','Foreign Key constraint')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('PK','Primary Key constraint')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('P','SQL Stored procedure')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('PC','Assembly (CLR) stored procedure')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('FN','SQL scalar function')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('FS','Assembly (CLR) scalar function')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('FT','Assembly (CLR) table-valued function')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('R','Rule (old-style, stand-alone)')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('RF','Replication-filter-procedure')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('S','System base table')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('SN','Synonym')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('SQ','Service queue')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('TA','Assembly (CLR) DML trigger')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('TR','SQL DML trigger')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('IF','SQL inline table-valued function')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('TF','SQL table-valued-function')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('U','Table (user-defined)')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('UQ','Unique constraint')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('V','View')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('X','Extended stored procedure')
insert into #objecttypes(otype,typedesc) values('IT','Internal table')
select otype,typedesc,count(s.type) as total
from #objecttypes
left join sys.objects s
on #objecttypes.otype collate Latin1_General_CI_AS = s.type collate Latin1_General_CI_AS
group by otype, typedesc
Saturday, 9 December 2006
TSQL : Checking for object existance...
IF EXISTS(SELECT Name FROM SysObjects WHERE Name='TEMP_MATCH_USERS' AND xType='U') BEGIN PRINT 'Dropping table dbo.TEMP_MATCH_USERS...' DROP TABLE [dbo].[TEMP_MATCH_USERS] END GO
Friday, 8 December 2006
SQL 2000 : Table Indexes via System Objects
SELECT SysUsers.[Name] AS Owner, Object_Name(SysIndexes.ID) AS TableName, SysIndexes.[Name] AS IndexName, [InDID] From SysIndexes Inner Join SysObjects On SysObjects.[ID]=SysIndexes.[ID] Inner Join SysUsers On SysUsers.[UID]=SysObjects.[UID] Where ObjectProperty(SysIndexes.[ID],'IsSystemTable')=0 And ObjectProperty(SysIndexes.[ID],'IsUserTable')=1 And [InDID]>0 And [InDID]<255 And [first] IS NOT NULL
Thursday, 7 December 2006
Table Row Counts via system objects
-- Get Table Row Counts via system objects SELECT sysobjects.name, sysindexes.rows FROM sysobjects INNER JOIN sysindexes ON sysobjects.id = sysindexes.id WHERE sysobjects.xtype = 'u' AND sysindexes.indid < 2 order by sysindexes.rows desc
Wednesday, 6 December 2006
Truncate all tables
/* Dynamic SQL to achieve this */ SELECT 'TRUNCATE TABLE [' +table_schema + '].[' + TABLE_NAME +']' FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
Sunday, 3 December 2006
TSQL Date Manipulation
SELECT DATEADD(dd, DATEDIFF(dd,0,getdate()), 0)
Monday of the Current Week
SELECT DATEADD(wk, DATEDIFF(wk,0,getdate()), 0)
First Day of Month
SELECT DATEADD(mm, DATEDIFF(mm,0,GETDATE()), 0)
Last Day of Month
SELECT DATEADD(dd,-1,DATEADD(mm, DATEDIFF(mm,0,GETDATE())+1, 0))
First Day of the Year
SELECT DATEADD(yy, DATEDIFF(yy,0,getdate()), 0)
Last Day of Year
SELECT DATEADD(dd,-1,DATEADD(yy, DATEDIFF(yy,0,GETDATE())+1, 0))
Further uses for CASE Statements
Computed Columns -
BMI = CASE WHEN (Height + Weight) IS NULL THEN 'Cannot Calculate' ELSE Weight / Height END
Conditional WHERE : Dealing with NULLs on the fly by using CASE statements.
For exact matches, check for columns being equal to themselves i.e. saying TRUE = TRUE
SELECT column1, column2, column3 FROM schema.table WHERE datecolumn BETWEEN @dateRangeFrom AND @dateRangeTo AND column4 = CASE WHEN @criteria IS NULL THEN column4 ELSE @criteria END
To use the LIKE clause in the same way, ISNULL can be used -
AND textcolumn LIKE ISNULL(@searchterm,'%')
This replaces an empty search term with the wildcard '%' which of course matches any term.
Conditional ORDER BY -
SELECT column1, column2, column3 FROM schema.table ORDER BY CASE WHEN @orderby = 'column1' THEN column1 WHEN @orderby = 'column2' THEN column2 WHEN @orderby = 'column3' THEN column3 END
Saturday, 2 December 2006
SQL 101 : Storage
A SQL database is made up of logical pages. A page is 8Kb (8192 bytes) in size and is used by both tables and indexes to store information. 8Kb is therefore the size of an input/output unit in SQL server.
*** Some special pages also exist for systems management purposes for example the ‘Global Allocation Map’, ‘Index Allocation Map’ and ‘Page Free Space’.
In versions up to SQL 2000, 8kb was the maximum row size in a table.
Prior to SQL 2005, defining a table with a larger row size is possible, but populating the columns fully was not.
For example, in SQL 7 - 2000 , the sql >
create table rubbishtable (
rubbishcolumn1 varchar (8000),
rubbishcolumn2 varchar (8000)
)
Returns the warning >
Warning: The table 'rubbishtable' has been created but its maximum row size (16023) exceeds the maximum number of bytes per row (8060). INSERT or UPDATE of a row in this table will fail if the resulting row length exceeds 8060 bytes.
SQL 2005
In SQL 2005, the page size is still 8Kb but you can exceed 8k per row.
This is achieved by moving the largest column to a second page into a ‘ROW_OVERFLOW_DATA unit’. The original page is then updated by adding a 24 byte pointer to this second page. This is known as the ‘IN_ROW_DATA allocation unit’.
You don’t see this functionality happening. ‘Oh great’ , ‘I can now fit more data into a row’ is likely to be a developer’s response to this new feature.
From a DBA’s point of view however, utilising this new functionality has performance implications.
Performing queries on tables where the data is split across pages will be marginally slower due to 2 pages being returned for each offending record.
Also, when updates are done which force the creation or deletion of overflow pages this will cause fragmentation in the database.
SQL Server Storage : Extents
An Extent is a group of 8 pages and hence is (8x8kb) 64Kb in size. This is the smallest unit of data SQL Server can allocate.
There are two types of extent.
Uniform Extent All 8 pages are assigned to a single object.
Mixed Extent More than 1 (small) object is placed inside the extent, ensuring space is not wasted.
SQL Server Storage : Files
Each datafile in a SQL database has 2 names, a logical file name (used to refer to the data store from transact SQL) and a physical one. The Physical one is the one stored on the operating system.
SQL databases have 3 filetypes.
Every database has a primary data store. The recommended (but not enforced) file extension is .MDF.
Some databases have (1 or more) secondary data files. The recommended (but not enforced) file extension is .NDF.
Log Files should have a .LDF extension. The log file (also known as the transaction log) holds a log of changes which may be helpful in recovering the datanase. When the recovery model is set to ‘simple’ they contain minimal information however.
SQL Server Storage : File Groups
File groups come in 2 flavours, ‘Primary’ or ‘User Defined’. Either of these can be the default file group i.e where all user objects are created (unless filegroup is specified).
File groups allow you to place heavily accessed tables in a different filegroup. Reasons for this could be to improve database performance (e.g housing the filegroup on a different disk array) or to backup that data separately.
Thursday, 30 November 2006
sp_MSforeachtable (Undocumented Stored Procedure)
The question mark represents the table name, examples are ;
sp_MSforeachtable @command1='print ''?'' dbcc checktable (''?'')'
sp_MSforeachtable @command1='print ''?'' truncate table [''?'']'
You can issue up to three commands to the stored procedure using parameters @command1 through @command3.
sp_MSforeachdb (Undocumented Stored Procedure)
The question mark represents the database name, for example ;
EXEC sp_MSforeachdb @command1='print ''?'' DBCC CHECKDB (''?'') '
Monday, 27 November 2006
SQL 2005 : CLR - External Access permissions
A .NET Framework error occurred during execution of user-defined routine or aggregate "SP_Backup":
System.Security.SecurityException: Request for the permission of type 'System.Security.Permissions.FileIOPermission, mscorlib, Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089' failed.
System.Security.SecurityException:
at DatabaseName.dbo.SP_Backup(Parameter1, Parmeter2, Parameter3...)
The CLR stored procedure is using XP_CMDShell to access the file system.
The permissions on the assembly therefore need to be increased to allow this.
Changing assembly permissions in Management Studio -
1) Navigate to (databasename) > Programmability > Assemblies > (expand)
2) Double click assembly name to get assembly properties.
3) Set permission set of assembly to 'external access'.
Changing assembly permissions in tsql -
GRANT EXTERNAL ACCESS ASSEMBLY TO AssemblyName
Configuring OpenRowset / OpenDatasource
"SQL Server blocked access to STATEMENT 'OpenRowset/OpenDatasource' of component 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries' because this component is turned off as part of the security configuration for this server. A system administrator can enable the use of 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries' by using sp_configure. For more information about enabling 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries', see "Surface Area Configuration" in SQL Server Books Online. "
Like the error says, here is where to enable in SAC >

Friday, 24 November 2006
CASE Basics
CASE @SecurityPass WHEN 2 THEN 'Admin' WHEN 1 THEN 'User' ELSE 'No Access' END
Searched Case Statement
CASE WHEN @Temp > 30 THEN 'Hot' WHEN @Temp < 0 THEN 'Freezing' ELSE 'Between' END
Using Openrowset to return usable columns from a stored procedure
use master
go
-- drop if already present
if object_id('master..waittype_summary') is not null
drop proc waittype_summary
-- create procedure
create proc waittype_summary as
select lastwaittype,
count(dbid) as process_count,
sum(cpu) as cpu
from master.dbo.sysprocesses
group by lastwaittype
order by sum(cpu) desc;
go
-- use openrowset to query the local procedure
select * from openrowset('SQLOLEDB', 'Trusted_Connection=Yes;Server=(local);Database=master', 'exec dbo.waittype_summary')
go
Although when running locally (as in this example), this is a daft idea (much easier to use a temp table) it demonstrates how to use openrowset.
Openrowset allows you to quickly connect to external data sources (access, excel, text files, oracle etc... ) without adding linked servers or importing data.
Under SQL 2005 however, we get this error -
Msg 15281, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
SQL Server blocked access to STATEMENT 'OpenRowset/OpenDatasource' of component 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries' because this component is turned off as part of the security configuration for this server. A system administrator can enable the use of 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries' by using sp_configure. For more information about enabling 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries', see "Surface Area Configuration" in SQL Server Books Online.
This is because SQL 2005 is more secure by default and the OpenRowset statement needs to be allowed via SAC (the Surface Area Configuration tool).
27/11/06 : More about that, here.
Thursday, 23 November 2006
Using temporary tables to return usable columns from a stored procedure
use master
go
-- clearup objects
if object_id('master..waittype_summary') is not null
drop proc waittype_summary
if object_id('tempdb..#waittype_summary_results') is not null
drop table #waittype_summary_results
go
-- procedure to fetch results from
create proc waittype_summary as
select lastwaittype,
count(dbid) as process_count,
sum(cpu) as cpu
from master.dbo.sysprocesses
group by lastwaittype
order by sum(cpu) desc;
go
-- temp table to store results
create table #waittype_summary_results
( lastwaittype varchar(30),
process_count int,
cpu int );
go
-- populate temp table
insert into #waittype_summary_results exec waittype_summary
-- display results
select * from #waittype_summary_results
Monday, 13 November 2006
Find tables with triggers
select schemas.name as schema_name, tables.name as table_name, triggers.name as trigger_name from sys.objects tables inner join sys.objects triggers on triggers.parent_object_id = tables.object_id inner join sys.schemas schemas on tables.schema_id = schemas.schema_id where triggers.type_desc = 'SQL_TRIGGER'
sql 2000
select
object_name(parent_obj) as tablename
,name as triggername
from sysobjects
where type = 'tr'
order by 1, 2
Saturday, 11 November 2006
Linked Server : RPC error
-- local server exec sp_executesql N'select @@version' -- remote server exec tranasctional2005...sp_executesql N'select @@version'" (1 row(s) affected) Msg 7411, Level 16, State 1, Line 4 Server 'tranasctional2005' is not configured for RPC. "
Right click, Linked server Name,
Select Properties.
Select Server Options page from the menu on the left.
Set RPC Out to 'True' on the pane on the right.

Friday, 3 November 2006
Shrinking Databases
If a database is online, the portion of the file in use is likely to be at the end of it, making reducing it's size impossible. SQL may have finished with the file and may just 'forgotten' to release this space. If this is the case, the following is worth a try.
Try the shrinkdatabase and shrinkfile methods below. They may achieve from partial to total success, depending on current activity i.e. any running processes.
Method 1 : Use the TSQL command dbcc shrinkdatabase >
i. Kill all running processes
ii. run the following sql -
dbcc shrinkdatabase (databasename, 'target percent')
Method 2 : Use the TSQL command dbcc shrinkfile to shrink the data & log files separately >
i. Kill all running processes
ii. run the following sql -
use tempdb go -- this command shrinks the primary data file dbcc shrinkfile (datafile, 'target size in MB') go -- this command shrinks the primary data file dbcc shrinkfile (datafilelog, 'target size in MB') go
* you can specify a target size of 0 and SQL will shrink the file as much as it can (although the first operation on that db will inevitably trigger automatic growth)
In SQL 2005+, these tasks can be done from Management Studio by Right clicking the database, selecting 'Tasks' then 'Shrink' followed by 'Database' or 'Files'.
If the files dont shrink, identify and stop any running processes you can afford to and repeat.
Running processes can be viewed in Activity Monitor (Server > Management > Activity Monitor in Management Studio).
If they have stalled and are stuck or you simply want to stop them, right click the process and select 'Kill Process'. Then click 'Yes' to confirm.
Shrinking TempDB
TempDB is a SQL Server System Database. It is a temporary database, used both as a work area for internal processing and to store temporary objects created by users.
It is recreated each time SQL Server starts.
Method 1 (Downtime allowed) -
Stop and Start the SQL Server service.
TempDB will be recreated at its initial size as set in the Files page of the Database Properties.
Method 2 (No Downtime) -
Kill as many processes as you can afford to, and use the TSQL commands e.g.
use tempdb go dbcc shrinkfile (tempdev, 'target size in MB') go dbcc shrinkfile (templog, 'target size in MB') go
( In SQL 2005+, this can be done from Management Studio by Right clicking the database, selecting 'Tasks' then 'Shrink' followed by 'Database' or 'Files'. )
Thursday, 2 November 2006
Networking : Black Hole Router
Ditto for network packets entering a 'Black Hole Router'.
A black hole router is one that simply drops packets destined for an ip address without even reporting that the host is not reachable.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black_hole_%28networking%29
Sunday, 29 October 2006
Bad Autogrowth
Imagine this default is still set on a production server, and you import a 50MB file when the datafile is at capacity.
The result is that 50 occurences of 1MB autogrow operations occur.
This is costly in terms of performance.
Now imagine multiple databases, all growing at varying rates (now that sounds like EVERY server doesn't it?)
As each of these datafiles 'expand' they take more disk space, grabbing the next available area on the disk. In this way, fragmentation of database files occurs.
As time goes on, simple database operations will rely more heavily on the disk as the server fetches data from logical files that are physically fragmented i.e. split.
Morals of this story...
1) Manually set data file sizes, allowing for expansion.
2) Review Disk/File fragmentation and perform disk maintenance
3) Do 1) & 2) regularly (stick reminders in your outlook!)
Saturday, 28 October 2006
Cryptographic Keys in SQL 2005

Basics :
Both 'Certificates' and 'Asymmetric keys' use Asymmetric encryption (RSA keys).
Certificates (sql 2000+) allow importing of keys from certificate files.
Asymmetric keys (sql 2005+) support importing keys from strong name files or sql assemblies.
Certificate files (.CER) are created using Microsoft Cerfificate Services (Windows Server 2000, 2003) or Active Directory Certificate Services (Windows 2008)
See my notes on cryptography, here.
Friday, 27 October 2006
Cryptography & Keys
Some Terminology -
Key - A sequence of bits, used by encryption algorithmns.
A 40 bit key > 10011110 01010101 00001010 01101001 00011100
Plaintext - The original message / content that was encrypted
Ciphertext - The encrypted version of a message
Cryptographic Strength - Time / Resources to break the ciphertext.
Cryptography works by applying a cipher or algorithm to plaintext to produce the ciphertext.
A key is used in conjunction with the algorithm. This way, the same algorithmn encrypts differently with different keys.
Cryptographic strength is dependent on a) algorithmn strength and b) key secrecy
Cryptographic Systems : Symmetric vs Asymmetric
Symmetric Cryptography (Private-key cryptography) -
Both sender & receiver have the SAME key.
Asymmetric Cryptography (Public-key cryptography)
Both sender & receiver have a PAIR of keys (public & private).
The public key is published (eg in the email signature of PGP users) whereas the private key is exactly that.
The receiver's key can decrypt messages encyrpted with the sender's key (& vice versa)
Any knowing the public key can Encrypt, but only people knowing the private key can Decrypt.
Asymmetric decryption is much slower and key sizes are bigger than symmetric keys.
n-bit Encryption
Simply, this refers to the key length used to encrypt data.
1 ASCII character = 8 bits, hence 128bit encyrption with an ASCII key means (8 x 13 = 128), a 13 character key length.
1 HEX character = 4 bits, hence 128bit encryption with a HEX key means (4 x 26 = 128), a 26 character key length
The number of combinations possible (i.e sequential attempts required to crack ciphertext via brute force) can be expressed as 2^n, where n is the represents the bit strength of the key.
For 40 bit encryption >
2^40 = 1099511627776 combinations
For 64 bit encryption >
2^64 = 18446744073709551616 combinations
For 128 bit encryption >
2^128 = 3.40282367 × 10^38 combinations
For 256 bit encryption >
2^256 = 1.1579208923731619542357098500869 x 10^77 combinations
Tuesday, 24 October 2006
UPDATE using inner SELECT
Demonstrated for simplicity here, but useful in the update criteria become complicated >
UPDATE person SET surname = updated.surname FROM person INNER JOIN ( SELECT correctdata.pk, correctdata.title, correctdata.surname, incorrectdata.title, incorrectdata.surname FROM person_import correctdata INNER JOIN person incorrectdata ON correctdata.pk = incorrectdata.pk WHERE incorrectdata.surname is null ) AS updated ON person.pk = updated.pk
Friday, 13 October 2006
SQL Code Searching - Views
-- view search SELECT TABLE_NAME FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS WHERE VIEW_DEFINITION LIKE '%q=%'
SQL Code Searching - Stored Procedures
-- sp search
select routine_name
from information_schema.routines
where routine_definition like '%code%'
and routine_type = 'procedure'
SQL Code Searching - Views
-- view search
select table_name
from information_schema.views
where view_definition like '%code%'
Saturday, 7 October 2006
SQL Schema Searching - Columns
-- column search select table_name from information_schema.columns where column_name = 'columnname'
Thursday, 5 October 2006
UltraEdit Macro - HTML Formatting
InsertMode ColumnModeOff HexOff UnixReOn TabsToSpaces Find "&" Replace All "&" Find ">" Replace All ">" Find "<" Replace All "<" Find " " Replace All " " Find "^p" Replace All " ^p"
Wednesday, 4 October 2006
2005 Maintenance Plan - Error 14234
Attempting to set up a simple backup job on another team's sql box. Went through all the wizard steps to create a backup job for them. Failed at the final hurdle, with >
Create maintenance plan failed.Additional information:Create failed for JobStep 'Subplan'. (Microsoft.SqlServer.MaintenancePlanTasks)
An exception occurred while executing a Transact-SQL statement or batch. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
The specified '@subsystem' is invalid (valid values are returned by sp_enum_sqlagent_subsystems). (Microsoft SQL Server, Error 14234)
This is due to not having Integration Services installed.
Bizarre that maintenance plans should need them, but there you go! Mind you, it was an unpatched system that I'm not responsible for, so maybe this error becomes more obvious in a later release.
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/909036Friday, 29 September 2006
SQL 101 : Email
SQL Server 2005 replaces SQL Mail with Database Mail which allows you to send to a SMTP Server directly.
Enabling Database Mail on a server (via SAC | via TSQL)
Configuring Database Mail via TSQL
SQL 2000
SQL Server 2000 features two ways to access email functionality, 'SQL Mail' and 'SQLAgentMail'.
Both components are MAPI applications, hence MAPI must be present on the server e.g. through Microsoft Outlook.
Through MAPI, SQL 2000 can talk to Exchange or POP3 mail servers.
Setting this up requires Outlook to be installed on the SQL Server, configured with a mailbox and profile name (log in as the account sql runs under to do so).
How to Configure SQL Mail
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/263556
In practice, MAPI can be a real pain both in terms of setup and reliability (a must if using for system notifications).
Therefore multiple solutions exist on the web to send email via other delivery mechanisms from SQL Stored procedures.
CDONTS (think Windows NT) requires a local 'virtual' SMTP server to be installed which is configured to forward emails to a physical one.
CDOSYS (Windows 2000 onwards) can send to a local or remote SMTP server.
Both methods require elavated privileges or the sysadmin role.
CDOSYS example
How to send e-mail without using SQL Mail in SQL Server
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/312839
Saturday, 23 September 2006
NOT IN vs NOT EXISTS vs OUTER JOIN
All are executed indentically according to the execution plan.
The third (outer join with null checking) is probably the most accedemically correct, though (IMHO) the least readable..
-- not in select * from Sales.SalesOrderDetail where SalesOrderID not in (select SalesOrderID from Sales.SalesOrderHeader) -- not exists select * from Sales.SalesOrderDetail SalesOrderDetail where not exists (select * from Sales.SalesOrderHeader SalesOrderHeader where SalesOrderDetail.SalesOrderID = SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID) -- outer join and NULL checking select * from Sales.SalesOrderDetail SalesOrderDetail left outer join Sales.SalesOrderHeader SalesOrderHeader on SalesOrderDetail.SalesOrderID = SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID where SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID is null
Friday, 22 September 2006
SQL 2000 > 2005 Linked Server Error
This occurs passing a NVARCHAR to sp_executesql on sql 2000 when linking to a 2005 instance.
Sql 2000 could not cope with the output returned by sql 2005 hence although the steps ran perfectly on their own.
declare @chvDataBaseName varchar(100) declare @sql nvarchar(2000) set @chvDataBaseName = 'northwind' -- backup on local server set @sql = N' BACKUP DATABASE ' + @chvDataBaseName set @sql = @sql + ' TO DISK = N''d:\tempmigrationfolder\' set @sql = @sql + @chvDataBaseName + '.BAK'' WITH NOFORMAT, INIT,' set @sql = @sql + ' NAME = N''Full Database Backup'',' set @sql = @sql + ' SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10' print @sql execute linked2005server.master.sp_executesql @sql
It is confirmed as a bug. I simply reversed my plan and ran the script from sql2005 performing the remote call on the sql 2000 databases.
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/896373
Saturday, 16 September 2006
SQL 2005 : Database Mail
By default, Database Mail is not enabled when SQL 2005 is installed.
You can enable it by the Surface Area Configuration Tool or by TSQL.
Friday, 15 September 2006
Enabling Database Mail via TSQL
-- allow advanced options sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; GO RECONFIGURE; GO -- enable database mail (0 disables , 1 enables) sp_configure 'Database Mail XPs', 1; GO RECONFIGURE GO -- hide advanced options again sp_configure 'show advanced options', 0; GO RECONFIGURE; GO
Thursday, 14 September 2006
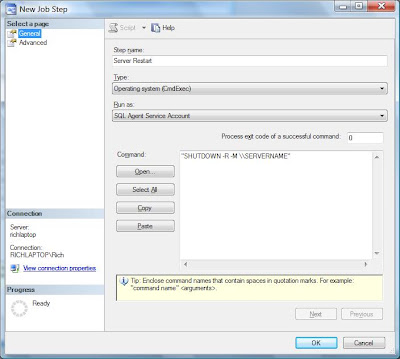
Enabling Database Mail via Surface Area Configuration
Start > Programs > Microsoft SQL Server 2005 > Configuration Tools > SQL Server Surface Area Configuration Tool
2) Open 'Surface Area Configuration for Features' (text link at bottom of page)
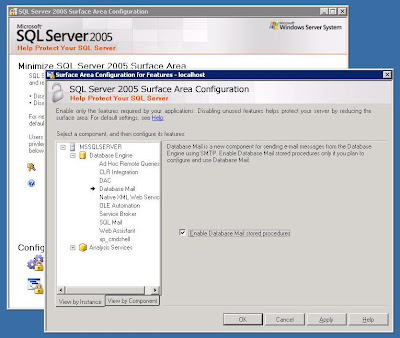
Click Database Mail and place an tick in the 'Enable Database Mail Stored Procedures'.
Click Apply then OK.
Sunday, 10 September 2006
Float as Varchar (Not Scientific)
SELECT CONVERT(varchar(100), CAST(@testFloat AS decimal(38,2)))or
SELECT STR(@testFloat, 38, 2)
Tuesday, 5 September 2006
Database Diagrams (SQL 2005)
Monday, 4 September 2006
Excel VBA - Code for importing a SQL Server table
Sub GetTableDataFromSQLServer()
' Declare the QueryTable object
Dim qt As QueryTable
' Set up the SQL Statement
sqlstring = 'select column1, column2, column3 from table'
' Set up the connection string, reference an ODBC connection
' Leave the name and password blank for NT authentication
connstring = 'ODBC;DSN=DataSouirceName;UID=;PWD=;Database=DatabaseName'
' Now implement the connection, run the query, and add
' the results to the spreadsheet starting at row A1
With ActiveSheet.QueryTables.Add(Connection:=connstring, Destination:=Range('A1'), Sql:=sqlstring)
.Refresh
End With
End Sub
Sunday, 3 September 2006
Configuring SQL Database Mail via TSQL
USE msdb GO DECLARE @mailprofilename VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @mailaccountname VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @mailaccountdescription VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @smtpserver VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @emailaddress VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @from VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @to VARCHAR(100) /* Declare everything as variables (makes it nice and easy to reuse script) */ SET @mailprofilename = 'DBMail Profile'; SET @mailaccountname = 'SQL Administrator'; SET @mailaccountdescription = 'for sql generated email notifications'; SET @smtpserver = '192.168.0.20'; SET @emailaddress = 'SQLAdmin@mydomain.net'; SET @from = 'SQL Administrator'; SET @to = 'recipient@mydomain.net'; -- add mail account EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_account_sp @account_name = @mailaccountname, @description = @mailaccountdescription, @email_address = @emailaddress, @display_name = @from, @mailserver_name = @smtpserver -- add mail profile EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profile_sp @profile_name = @mailprofilename -- associate mail account & mail profile together EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profileaccount_sp @profile_name = @mailprofilename, @account_name = @mailaccountname, @sequence_number = 1 ; -- send test email EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @recipients = @to, @subject = 'rabbit, rabbit, rabbit, rabbit', @body = 'bunny, bunny, bunny, bunny', @profile_name = @mailprofilename
Friday, 1 September 2006
Display ASCII table script
if object_id('tempdb..#results') is not null
drop table #results
create table #results (asciicode smallint,displaychar char)
declare @intCounter smallint
set @intCounter = 1
while @intCounter <= 255
begin
insert into #results (asciicode,displaychar)
select @intCounter, char(@intCounter)
set @intCounter = @intCounter + 1
end
select asciicode, displaychar from #results
Thursday, 31 August 2006
Wednesday, 30 August 2006
Sunday, 27 August 2006
TSQL : Searching Job Steps
Use to locate sql code performing a certain function.
use msdb go select sysjobs.name, sysjobsteps.command from sysjobs inner join sysjobsteps on sysjobs.job_id = sysjobsteps.job_id where command like '%searchstring%' order by name
Reports In Management Studio 2005
Support
No support for SQL 2000 instances
No support for databases prior to Compatibility Mode 90 (Restores of SQL 2000 databases on SQL 2005)
Report Types
Standard Reports - Inbuilt, see screenshots below.
Custom Reports (SP2 onwards) - Run a .RDL file (Reporting Services Report) within the context of the current server in Management St
Accessing Reports
Right click a node in Object Explorer to get Reports Menu
Standard Reports, Custom Reports and shortcuts to the most recently accessed reports are the options.
The list of available Reports is context sensitive e.g 'Service Broker Statistics' only appears when selecting reports from the 'Service Broker' node.
Standard Reports
17 Database Reports >
Navigating to Reports : (Databases > [database name] > )

Disk Usage :

Disk Usage by Top Tables :

Disk Usage by Table :

Disk Usage by Partition :

Backup and Restore Events :

All Transactions :

Top Transactions by Age :

All Blocking Transactions :

Top Transactions by Age :

Top Transactions by Blocked Transactions Count :

Top Transactions by Locks Count :

Resource Locking Statistics by Objects :

Object Execute Statistics :

Database Consistency history :

Index Usage Statistics :

Index Physical Statistics :

Schema Change history :

User Statistics :

Databases > [database name] > Service Broker Node >
Service Broker Statistics :

Server Reports >
Security > Logins >
Login Statistics :

Login Failures :

Resource Locking Statistics by login :

Management >
Tasks :

Number of Errors :

Notification Services >
General :

SQL Server Agent >
Job Steps Execution History :

Top Jobs :

Thursday, 24 August 2006
TSQL : Negate Time from DateTime column
SELECT DATEADD(dd, DATEDIFF(dd, '1900-01-01', GETDATE()),'1900-01-01')
update! more efficient :
SELECT DATEADD(dd, DATEDIFF(dd,0,GETDATE()), 0)
original version :
SELECT CAST(FLOOR(CAST(GETDATE() AS FLOAT)) AS DATETIME)
Saturday, 19 August 2006
SQL 2000 ; Replication Clearup Script
DECLARE @TabName varchar(255) DECLARE @ConstName varchar(255) DECLARE @SQL nvarchar(255) DECLARE @Cnt as int DECLARE @DBNAME as varchar(255) SET @DBNAME = '' use (databasename) DECLARE Const_cursor CURSOR FOR SELECT O_Table.[Name], O_Const.[Name] FROM sysConstraints C INNER JOIN sysObjects O_Table ON O_Table.[ID] = C.[ID] INNER JOIN sysobjects O_Const ON O_Const.[ID] = C.ConstID WHERE O_Const.[Name] LIKE 'DF__' + LEFT(O_Table.Name,9) + '__msrep__%' ORDER BY 1,2 SET @Cnt = 0 OPEN Const_cursor FETCH NEXT FROM Const_cursor INTO @TabName, @ConstName WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN PRINT 'Processing ' + @TabName SET @Cnt = @Cnt + 1 --First we need to drop the constraint SELECT @SQL = 'ALTER TABLE ' + @DBNAME + @TabName + ' DROP CONSTRAINT ' + @ConstName exec sp_executesql @SQL PRINT @SQL --Now drop the unneeded column SELECT @SQL = 'ALTER TABLE ' + @DBNAME + @TabName + ' DROP COLUMN msrepl_tran_version' exec sp_executesql @SQL PRINT @SQL FETCH NEXT FROM Const_cursor INTO @TabName, @ConstName END PRINT '' PRINT cast(@Cnt as varchar(3)) + ' Tables Processed' CLOSE Const_cursor DEALLOCATE Const_cursor GO
Thursday, 10 August 2006
USP_FixUsers :: Fix All Orphanned Users
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.USP_FixUsers AS /* Based on the widely available sp_fixusers */ BEGIN DECLARE @username varchar(25) DECLARE fixusers CURSOR FOR SELECT UserName = name FROM sysusers WHERE issqluser = 1 and (sid is not null and sid <> 0x0) and suser_sname(sid) is null ORDER BY name OPEN fixusers FETCH NEXT FROM fixusers INTO @username WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN EXEC sp_change_users_login 'update_one', @username, @username FETCH NEXT FROM fixusers INTO @username END CLOSE fixusers DEALLOCATE fixusers END GO
Wednesday, 9 August 2006
SQL connectivity issues
http://blogs.msdn.com/sql_protocols/archive/2008/04/30/steps-to-troubleshoot-connectivity-issues.aspx
Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues in SQL Server 2005 - Part I
http://blogs.msdn.com/sql_protocols/archive/2005/10/22/483684.aspx
Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues in SQL Server 2005 - Part II
http://blogs.msdn.com/sql_protocols/archive/2005/10/29/486861.aspx
Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues in SQL Server 2005 - Part III
http://blogs.msdn.com/sql_protocols/archive/2005/12/22/506607.aspx
Outlook 2003+ : Customizing Startup Folder
START /MAX '' 'C:\Program files\Microsoft Office\OFFICE11\OUTLOOK.EXE' START /MAX '' 'C:\Program files\Microsoft Office\OFFICE11\OUTLOOK.EXE' /select outlook:tasks START /MAX '' 'C:\Program files\Microsoft Office\OFFICE11\OUTLOOK.EXE' /select outlook:calendar START /MAX '' 'C:\Program files\Microsoft Office\OFFICE11\OUTLOOK.EXE' /select outlook:contacts START /MAX '' 'C:\Program files\Microsoft Office\OFFICE11\OUTLOOK.EXE' /select outlook:notesPut your preferred options in a batch file to use multiple instances of outook (useful as can switch between outlook functionality on the grouped taskbar in xp).
Saturday, 5 August 2006
Thursday, 3 August 2006
Dynamic SQL to set all databases to Simple recovery mode
-- Dynamic SQL to set all databases to Simple recovery mode
-- set all to simple
-- use this sql to generate to sql to perform this task.
use master
SELECT 'ALTER DATABASE [' + name + '] SET RECOVERY SIMPLE' from master..sysdatabases where name not in ('master','model','msdb','tempdb')
Wednesday, 2 August 2006
Good Practice - Procedure Commenting
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[USP_ProcedureName] /**/ AS BEGIN -- Do stuff here!!! END USP_ProcedureName Stored Procedure What the procedure does. 1 05/05/2006 Joe Bloggs Original Version 2 23/06/2006 Fred Bloggs Changed some code 3 01/08/2006 Joe Bloggs Changed some more code
Saturday, 22 July 2006
TSQL : Generating GUIDs
SELECT NewID()
8E8DDFD9-568C-4815-832B-551604AEFB9F
Friday, 21 July 2006
sp_changeobjectowner
use :
sp_changeobjectowner [objectname] , [new owner]
example :
sp_changeobjectowner 'fasttrackuser.FastTrackPackageDocumentsCombinations', 'dbo'
remarks :
must have appropriate permissions to perform this action.
Sunday, 16 July 2006
USP_DropTableConstraints (SQL 2000 Version)
CREATE PROCEDURE USP_DropTableConstraints @tablename VARCHAR(128)
AS
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @constraintname VARCHAR(128),
@sqlcmd VARCHAR(1024)
DECLARE CONSTRAINTSCURSOR CURSOR FOR
SELECT NAME
FROM SYSOBJECTS
WHERE XTYPE IN ('C','F','PK','UQ',
'D')
AND (STATUS & 64) = 0
AND PARENT_OBJ = OBJECT_ID(@tablename)
-- nb : xtype refers to CHECK, FOREIGN KEY, PRIMARY KEY, UNIQUE, and DEFAULT constraints.
OPEN CONSTRAINTSCURSOR
FETCH NEXT FROM CONSTRAINTSCURSOR
INTO @constraintname
WHILE (@@FETCH_STATUS = 0)
BEGIN
SELECT @sqlcmd = 'ALTER TABLE ' + @tablename + ' DROP CONSTRAINT ' + @constraintname
EXEC( @sqlcmd)
FETCH NEXT FROM CONSTRAINTSCURSOR
INTO @constraintname
END
CLOSE CONSTRAINTSCURSOR
DEALLOCATE CONSTRAINTSCURSOR
RETURN 0
GO
Wednesday, 12 July 2006
Good Practice - Schema Scripting
Here are some examples for those supplying schema modifications -
example 1 - When replacing an database object, check for its existance
and drop it first before attempting to create it.
IF EXISTS(select * from information_schema.tables
where table_name ='FORECAST_BREAKDOWN')
BEGIN
DROP TABLE [dbo].[FORECAST_BREAKDOWN]
END
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[FORECAST_BREAKDOWN](
[STACK_ID] [numeric](10, 0) NOT NULL,
[PLOT_CODE] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[FB_AMOUNT] [numeric](35, 10) NOT NULL CONSTRAINT [DF__FORECAST___FB_AM__54EB90A0] DEFAULT ((0)),
[DESCRIPTION] [varchar](255) NULL,
[FB_DATE] [datetime] NULL)
go
example 2 - Check for the existence of a column before attempting to add it.
IF NOT EXISTS(select * from information_schema.columns
where table_name ='forecast_breakdown'
and column_name = 'srno')
BEGIN
PRINT 'Column not present, creating...'
ALTER TABLE [FORECAST_BREAKDOWN] ADD SRNO INT
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT 'Column already present'
END
These examples show how to script table and column changes. There are many more INFORMATION_SCHEMA views documented here > http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186778.aspx
Friday, 7 July 2006
Restore TSQL
FROM DISK = N'c:\database.bak'
WITH MOVE 'databasename' TO 'D:\data\databasename.mdf',
MOVE 'databasename_log' TO 'E:\logs\databasename.ldf', NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
Tuesday, 4 July 2006
SQL : Data Search Script
/*
dynamic sql to search for data
*/
select 'if exists (select 1 from [' +
table_name +
'] where ' +
column_name +
' like ''%Fred Bloggs%'' ) print ''' +
table_name +
'/' +
column_name +
'''' +
char(10) +
'go'
from information_schema.columns
where data_type in ('ntext','smallint','int','char', 'varchar', 'nvchar', 'nvarchar')
and table_schema = 'dbo'
and column_name <> 'order'
Monday, 3 July 2006
Stored procedure permissions script
select 'Grant EXEC on ' + name + ' to MyUser' from sysobjects where type = 'P'
Saturday, 1 July 2006
Full Text Indexes - Indexing Priority
sp_fulltext_service 'resource_usage' , n
where n is a value from 1 to 5 representing low to high priority respectively.
Thursday, 29 June 2006
Disabling the annoying system beep!
Go to the dos prompt (START > RUN > type 'CMD' {Enter]
Run these 2 commands >
net stop beep [ENTER]
sc config beep start= disabled [ENTER]
Personally, i pasted those two command lines into a batch file and ran it on my machines (physical and virtual).
Monday, 26 June 2006
LDAP Error
" Msg 7346, Level 16, State 2, Line 1
Cannot get the data of the row from the OLE DB provider "ADSDSOObject" for linked server "linkedservername".
Could not convert the data value due to reasons other than sign mismatch or overflow. "
Was retrieving data from Active Directory via a linked server in SQL.
Bottom line is that you cannot use OPENQUERY to get multivalued attributes or columns containing date information from AD.
Sunday, 25 June 2006
Querying Active Directory Group membership from SQL
Inspired from (& based on) code @ http://codebetter.com/blogs/brendan.tompkins/archive/2003/12/19/4746.aspx
This code looks at an LDAP v2 source eg; Windows 2000 and fetches users, groups and membership information.
You need to set up a linked server called 'ADSI' to get this to function.
Setting up the linked server -
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'ADSI', @srvproduct=N'Active Directory Services 2.5', @provider=N'ADSDSOObject', @datasrc=N'adsdatasource' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'ADSI',@useself=N'False',@locallogin=NULL,@rmtuser=N'domain\user',@rmtpassword='########' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'collation compatible', @optvalue=N'false' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'data access', @optvalue=N'true' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'dist', @optvalue=N'false' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'pub', @optvalue=N'false' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'rpc', @optvalue=N'false' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'rpc out', @optvalue=N'false' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'sub', @optvalue=N'false' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'connect timeout', @optvalue=N'0' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'collation name', @optvalue=null GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'lazy schema validation', @optvalue=N'false' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'query timeout', @optvalue=N'0' GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ADSI', @optname=N'use remote collation', @optvalue=N'true'
The code itself -
-- Configure AD Domain to search
DECLARE @strDC NVARCHAR(100)
SET @strDC = 'dc=domain,dc=co,dc=uk'
-- Declare Variables
DECLARE @chvAlphaChars VARCHAR(60),
@chvSearch VARCHAR(10),
@chvSearchLevel1 VARCHAR(1),
@chvSearchLevel2 VARCHAR(1),
@chvSearchLevel3 VARCHAR(1),
@intcountLevel1 INT,
@intcountLevel2 INT,
@intcountLevel3 INT,
@intRowCount INT,
@strSQL NVARCHAR(4000),
@strADSISQL NVARCHAR(4000),
@Login VARBINARY(85),
@CN VARCHAR(512),
@CT INT,
@ADRoot VARCHAR(255)
-- Declare temp tables
IF EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM TEMPDB.DBO.SYSOBJECTS
WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID('tempdb.dbo.#LDAP_AD_V2_Users'))
DROP TABLE #LDAP_AD_V2_USERS
CREATE TABLE [DBO].[#LDAP_AD_V2_USERS] (
[ROW_ID] [INT] IDENTITY ( 1,1 ) NOT NULL,
[SID] [VARBINARY](85) NULL,
[SAMACCOUNTNAME] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[CN] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[SN] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[DISPLAYNAME] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[GIVENNAME] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[TELEPHONENUMBER] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[ADSPATH] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[HOMEDIRECTORY] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[MAIL] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[MEMBEROF] [NVARCHAR](256) NULL,
[PRIMARYGROUPID] [INT],
[CREATETIMESTAMP] DATETIME)
ON [PRIMARY]
IF EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM TEMPDB.DBO.SYSOBJECTS
WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID('tempdb.dbo.#LDAP_AD_V2_Groups'))
DROP TABLE #LDAP_AD_V2_GROUPS
CREATE TABLE [DBO].[#LDAP_AD_V2_GROUPS] (
[ID] [INT] IDENTITY ( 1,1 ) NOT NULL,
[LOGIN] [VARCHAR](512) NULL,
[EMAIL] [VARCHAR](255) NULL,
[ACCTNAME] [VARCHAR](512) NULL,
[DISTNAME] [VARCHAR](512) NULL,
[CREATEDDATE] [DATETIME] NULL,
[CHANGEDDATE] [DATETIME] NULL,
[MGR] [VARCHAR](512) NULL,
[SID] [VARBINARY](85) NULL)
ON [PRIMARY]
IF EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM TEMPDB.DBO.SYSOBJECTS
WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID('tempdb.dbo.#LDAP_AD_V2_UserGroups'))
DROP TABLE #LDAP_AD_V2_USERGROUPS
CREATE TABLE [DBO].[#LDAP_AD_V2_USERGROUPS] (
[USERLOGIN] [VARBINARY](85) NOT NULL,
[GROUPLOGIN] [VARBINARY](85) NULL)
ON [PRIMARY]
-- POPULATION OF USERS
-- Search letters to cycle through
-- any chars, but the first char must be a space
SET @chvAlphaChars = ' ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ.-_`0123456789'
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- start on non space char
SET @intcountLevel1 = 2
-- first level loop
WHILE @intcountLevel1 <= LEN(@chvAlphaChars)
BEGIN
-- get first level char
SET @chvSearchLevel1 = SUBSTRING(@chvAlphaChars,@intcountLevel1,1)
-- reset start on space
SET @intcountLevel2 = 1
-- second level loop
WHILE @intcountLevel2 <= LEN(@chvAlphaChars)
BEGIN
-- reset start on space
SET @intcountLevel3 = 1
-- third level loop
WHILE @intcountLevel3 <= LEN(@chvAlphaChars)
BEGIN
-- setup the string to search for. By using the trim function we can form each level depending on no records
-- eg A 99, B 1000 > BA 9, BB 20 etc
-- trim the spaces forming just A, B, C ; AA, AB for search etc
SET @chvSearchLevel1 = SUBSTRING(@chvAlphaChars,@intcountLevel1,1)
SET @chvSearchLevel2 = RTRIM(SUBSTRING(@chvAlphaChars,@intcountLevel2,1))
SET @chvSearchLevel3 = RTRIM(SUBSTRING(@chvAlphaChars,@intcountLevel3,1))
SET @chvSearch = @chvSearchLevel1 + @chvSearchLevel2 + @chvSearchLevel3
SET @strADSISQL = 'select objectSid,cn,sn,displayName, sAMAccountName, givenName, telephoneNumber, adspath, homedirectory, mail, primarygroupid, createTimeStamp '
+ CHAR(13) + 'from ''''LDAP://' + @strDC + ''''' '
+ CHAR(13) + 'where objectCategory = ''''Person'''' '
+ CHAR(13) + 'and objectClass = ''''user'''' '
+ CHAR(13) + 'and sAMAccountName = ''''' + @chvSearch + '*'''' '
SET @strSQL = 'insert into #LDAP_AD_V2_Users (sid,cn,sn,displayName, sAMAccountName, givenName, telephoneNumber, adspath, homedirectory, mail, primarygroupid, createTimeStamp) '
+ CHAR(13) + 'select objectSid,cn,sn,displayName, sAMAccountName, givenName, telephoneNumber, adspath, homedirectory, mail, primarygroupid, createTimeStamp '
+ CHAR(13) + 'from openquery(ADSI,''' + @strADSISQL + ''' ) '
+ CHAR(13) + 'order by sAMAccountName'
EXEC SP_EXECUTESQL @strSQL
SET @intRowCount = @@ROWCOUNT
-- prints what string is being searched for : no of inserts
-- PRINT @chvSearch + ' : ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR,@intRowCount)
-- if searched on @chvSearchLevel1 and under 1000 then everything is fine so skip search2 to next search1 eg A > B
IF @intRowCount < 1000
AND @chvSearchLevel2 = ''
SET @intcountLevel2 = @intcountLevel2 + 100
-- if searched on @chvSearchLevel2 and under 1000 then everything is fine so skip to next search2 eg AA > AB
IF @intRowCount < 1000
AND @chvSearchLevel3 = ''
SET @intcountLevel3 = @intcountLevel3 + 100
-- else over 1000 so increment third level
SET @intcountLevel3 = @intcountLevel3 + 1
END
-- increment next second level char
SET @intcountLevel2 = @intcountLevel2 + 1
END
-- increment next first level char
SET @intcountLevel1 = @intcountLevel1 + 1
END
-- POPULATION OF GROUPS
SET @strADSISQL = 'select objectSid, managedBy, whenChanged, whenCreated, distinguishedName, name, samAccountName, mail '
+ CHAR(13) + 'FROM ''''LDAP://' + @strDC + ''''' '
+ CHAR(13) + 'WHERE objectCategory = ''''Group'''' '
SET @strSQL = 'insert into #LDAP_AD_V2_Groups (sid,mgr,changeddate,createddate,distname,acctname,email,login) '
+ CHAR(13) + 'select objectSid,managedBy,whenChanged,whenCreated,distinguishedName,name,mail,samAccountName '
+ CHAR(13) + 'from openquery(ADSI,''' + @strADSISQL + ''' ) '
+ CHAR(13) + 'order by sAMAccountName'
-- PRINT @strSQL
EXEC SP_EXECUTESQL @strSQL
-- POPULATION OF USER > GROUPS RELATIONSHIP TABLE
IF EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM TEMPDB.DBO.SYSOBJECTS
WHERE ID = OBJECT_ID('tempdb.dbo.#CT'))
DROP TABLE #CT
-- Create a temporary table to hold AD user SID values
CREATE TABLE #CT (CT VARBINARY(85))
-- Declare and open a cursor to step through the list of Active Directory groups
DECLARE CURGROUPS CURSOR FOR
SELECT SID,
DISTNAME
FROM #LDAP_AD_V2_GROUPS
ORDER BY LOGIN
OPEN CURGROUPS
FETCH NEXT FROM CURGROUPS
INTO @Login,
@CN
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Empty the temp table
TRUNCATE TABLE #CT
-- Build a SQL statement to insert the SID values directly from the linked server into the temp table
SET @strsql = 'INSERT #CT
SELECT *
FROM OPENQUERY (
ADSI,
''SELECT objectSid
FROM ''''LDAP://' + @strDC + '''''
WHERE objectCategory = ''''User''''
AND memberof=''''' + REPLACE(@CN,'''','''''''''') + ''''''')'
EXEC( @strsql)
-- Select the number of records inserted. If this value is less than 1000 then there is no need
-- to execute the OLE calls, and we simply copy the values into the correlation table.
SELECT @CT = COUNT(* )
FROM #CT
--PRINT @ct
--PRINT @strsql
IF @CT <> 0
BEGIN
INSERT #LDAP_AD_V2_USERGROUPS
(USERLOGIN,
GROUPLOGIN)
SELECT CT,
@Login
FROM #CT
WHERE CT IS NOT NULL
END
FETCH NEXT FROM CURGROUPS
INTO @Login,
@CN
END
CURSORERROR:
CLOSE CURGROUPS
DEALLOCATE CURGROUPS
DROP TABLE #CT
/*
-- Individual SQL Statements to see users, groups & relationships
select * from #LDAP_AD_V2_Users
select * from #LDAP_AD_V2_Groups
select * from #LDAP_AD_V2_UserGroups
*/
-- Final Query to tie together the 3 tables and produce a report of group membership
SELECT #LDAP_AD_V2_GROUPS.ACCTNAME AS GROUPNAME,
#LDAP_AD_V2_USERS.SAMACCOUNTNAME AS USERACCOUNT
FROM #LDAP_AD_V2_USERGROUPS
INNER JOIN #LDAP_AD_V2_USERS
ON #LDAP_AD_V2_USERGROUPS.USERLOGIN = #LDAP_AD_V2_USERS.SID
INNER JOIN #LDAP_AD_V2_GROUPS
ON #LDAP_AD_V2_USERGROUPS.GROUPLOGIN = #LDAP_AD_V2_GROUPS.SID
ORDER BY #LDAP_AD_V2_GROUPS.ACCTNAME,
#LDAP_AD_V2_USERS.SAMACCOUNTNAME
Friday, 23 June 2006
SQL 101 : Date Formatting
-- SQL DateTime Validation
SELECT CAST('2006-03-31' AS datetime) -- Succeeds, 31 days in March
SELECT CAST('2006-04-31' AS datetime) -- Fails, only 30 days in April
SELECT CAST('2006-02-29' AS datetime) -- Fails, No 29th day in Feb 2006
SELECT CAST('2004-02-29' AS datetime) -- Succeeds, was a leap year
SELECT CAST('2002-02-29' AS datetime) -- Fails, No 29th day in Feb 2002
SELECT CAST('2000-02-29' AS datetime) -- Succeeds, was a leap year
When language is set to us_english, date format of 'mdy' expects the month to be provided before the day.
SET LANGUAGE us_english -- Changed language setting to us_english.
SELECT CAST('2006-03-31' AS datetime) -- works
SELECT CAST('03-31-2006' AS datetime) -- works
SELECT CAST('31-03-2006' AS datetime) -- fails
When language is set to british, date format of 'dmy' expects the day to be provided before the month.
SET LANGUAGE british -- Changed language setting to British.
SELECT CAST('2006-03-31' AS datetime) -- fails
SELECT CAST('2006-31-03' AS datetime) -- works
SELECT CAST('31-03-2006' AS datetime) -- works
In both of these cases, SQL correctly interprets the year, whether at the start or end of the string.
The failures generate -
Msg 242, Level 16, State 3, Line 7
The conversion of a char data type to a datetime data type resulted in an out-of-range datetime value.
Using set dateformat to override the language setting -
SET DATEFORMAT 'dmy'
-- example
SET LANGUAGE us_english -- Changed language setting to us_english.
SET DATEFORMAT 'dmy'
SELECT CAST('31-03-2006' AS datetime) -- now succeeds.
Best Practice is to use a language neutral date format -
-- ISO 8601 format doesnt care about language >
SELECT CAST('2006-03-31T00:00:00' AS datetime)
-- Neither does removing the '-'
SELECT CAST('20060331' AS datetime)
More on language neutral date formats here - http://www.karaszi.com/SQLServer/info_datetime.asp
2 ways to get the current time & date -
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP SELECT getdate()
Tuesday, 20 June 2006
FTP Server : Filezilla
Download it here > http://sourceforge.net/projects/filezilla/
They also do a free FTP client hence I'm ditching SmartFTP for Filezilla >
Yes, I know you can ftp from within I.E and the OS, but this is the real world, where usability and reliability rule :)
Monday, 19 June 2006
SQL : Make all columns NULLable
SELECT 'alter table ' + TABLE_NAME + ' alter column ' + COLUMN_NAME + ' ' + data_type + '(' + CAST(CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH as VARCHAR(5)) + ') NULL'
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
WHERE IS_NULLABLE = 'NO'
AND DATA_TYPE IN ('VARCHAR','CHAR')
Saturday, 17 June 2006
Dynamic SQL - Passing a parameter using sp_execute
/*
Dynamic SQL : Passing a parameter to sp_execute
Example uses AdventureWorks db
*/
exec sp_executesql N'SELECT
e.[EmployeeID]
,c.[Title]
,c.[FirstName]
,c.[MiddleName]
,c.[LastName]
,c.[Suffix]
,e.[Title] AS [JobTitle]
,c.[Phone]
,c.[EmailAddress]
,c.[EmailPromotion]
,a.[AddressLine1]
,a.[AddressLine2]
,a.[City]
,sp.[Name] AS [StateProvinceName]
,a.[PostalCode]
,cr.[Name] AS [CountryRegionName]
,c.[AdditionalContactInfo]
FROM
[HumanResources].[Employee] e
INNER JOIN [Person].[Contact] c
ON c.[ContactID] = e.[ContactID]
INNER JOIN [HumanResources].[EmployeeAddress] ea
ON e.[EmployeeID] = ea.[EmployeeID]
INNER JOIN [Person].[Address] a
ON ea.[AddressID] = a.[AddressID]
INNER JOIN [Person].[StateProvince] sp
ON sp.[StateProvinceID] = a.[StateProvinceID]
INNER JOIN [Person].[CountryRegion] cr
ON cr.[CountryRegionCode] = sp.[CountryRegionCode]
AND cr.[Name] = @Region',N'@Region varchar(20)','Germany'
Thursday, 15 June 2006
Send email from TSQL
This script assumes you have set up database mail with an account name of 'SQL Administrator' and provided valid SMTP details.
-- declare variables DECLARE @chvFrom VARCHAR(255) DECLARE @chvTo VARCHAR(255) DECLARE @chvSubject VARCHAR(255) DECLARE @chvBody VARCHAR(8000) -- set values SET @chvFrom = 'SQLAdmin@mydomain.net' SET @chvTo = 'recipient@mydomain.net' SET @chvSubject = 'Test email from ' + @@SERVERNAME SET @chvBody = 'test body text' -- send the mail EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @profile_name='SQL Administrator', @recipients=@chvTo, @body=@chvBody,@subject=@chvSubject, @importance='High'
Wednesday, 7 June 2006
ISO Image Tools
The latest updates and installers are taking the form of ISO files i.e. image files of installation media. These are the FREE tools I rate for dealing with ISO files.
Daemon Tools - Emulates an optical drive so you can use an image without burning to disc.
DoISO - Create ISO files from a given directory.
ImgBurn - Burns ISOs to disc and extracts images from discs. Especially good with 'difficult' discs. Used to be known as DVD Decrypter.
Sunday, 4 June 2006
SQL 2005+ - TRY CATCH Error detection
SQL 2005 implements the TRY CATCH syntax in the same way as javascript, c++ and subsequently the .NET languages.
For example, using AdventureWorks, I purposely attempt to delete a record I shouldnt, and receive an error -
DELETE Person.Address WHERE AddressID = 1
Msg 547, Level 16, State 0, Line 2
The DELETE statement conflicted with the REFERENCE constraint "FK_EmployeeAddress_Address_AddressID". The conflict occurred in database "AdventureWorks", table "HumanResources.EmployeeAddress", column 'AddressID'.
The statement has been terminated.
@@ERROR only contains the error in the very next statement after the error, hence to both examine & display the value I have to assign it to a local variable -
TSQL Programming to catch the error -
DECLARE @ErrorResult INTEGER DELETE Person.Address WHERE AddressID = 1 SET @ErrorResult = @@ERROR IF @ErrorResult <>0 BEGIN PRINT 'Error ' + CAST(@ErrorResult AS VARCHAR(10)) + ' : Could not Delete record' END
Msg 547, Level 16, State 0, Line 2
The DELETE statement conflicted with the REFERENCE constraint "FK_EmployeeAddress_Address_AddressID". The conflict occurred in database "AdventureWorks", table "HumanResources.EmployeeAddress", column 'AddressID'.
The statement has been terminated.
Error 547 : Could not Delete record
Note : both the SQL Error and my message are returned.
Using TRY/CATCH however, the error can be caught and the script continues -
BEGIN TRY
-- Attempt delete of referenced record.
DELETE Person.Address WHERE AddressID = 1
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
-- Do alternate action.
PRINT 'Could not Delete record'
END CATCH
Much tidier, only my error message is returned -
Error 547 : Could not Delete record
Friday, 2 June 2006
Accessing AD Users & Computers on a Member Server
Start > Run > MMC [enter]
File > Add / Remove Snap-In
Click 'Add' to see available snap-ins.
Select 'Active Directory Users and Computers'
Click the 'Add', then 'Close' and finally 'OK'.
The functionality available will obviously depend on who you are logged in as.
Thursday, 1 June 2006
Removing Database Backup History
Once a backup has been archived, i.e. moved away from the location it was originally written to, there is no need to keep the record of the backup. Infact, these records build up, increasing the size of the msdb database (quickly if frequent transaction log backups are performed).
To see the date range of backup history you have, us this query -
use msdb SELECT a.name , MIN(b.backup_finish_date) EarliestSuccessfulBackup , MAX(b.backup_finish_date) LatestSuccessfulBackup FROM master..sysdatabases a LEFT OUTER JOIN msdb..backupset b ON a.name = b.database_name GROUP BY a.name ORDER BY a.nameTo prevent this occuring, use system stored procedure sp_delete_backuphistory and pass it the date of the oldest record you want to keep.
use msdb go exec sp_delete_backuphistory '1/1/2006'If a database is removed altogether, zap it's backup history like this -
exec msdb.dbo.sp_delete_database_backuphistory 'Adventureworks'If backups are archived regularly, schedule a job to remove excess history records, like this -
-- Calculate date to be used when removing records, -- This example deletes records over a month old. DECLARE @dtOldest_date DATETIME SET @dtOldest_date = dateadd(month, -1, getdate()) EXEC msdb..sp_delete_backuphistory @dtOldest_dateNB :SQL 2005+ addresses this by providing cleanup tasks in the Maintainence Plans (if you use them).